Workforce Analytics
Last updated on: 22nd July, 2025 | Analytics Insights | Neeraj Chachlani, Class of 2018 << back to blog

Published on: 22nd October, 2017
Overview
In today’s competitive environment, businesses must effectively allocate workforce to achieve success. This requirement has radically changed the role of HR managers from functional to transformational. In addition to hiring right talent, HR manager is expected to perform roles of a brand builder, a communicator, a motivator, a collaborator and more importantly an analyst. Strategic decision making of HR is now assisted with the relentless flow of data and analytics.
To describe a tangible link between people strategy and organization performance, managers use workforce analytics. Workforce analytics can be formally defined as systematic computation of data for guiding businesses in delivering best possible performance by using its human capital efficiently. To serve this purpose, HR professionals must recognize, track and measure the information that is more relevant and important.
Current scenario
Generic best practice models used by HR professionals need to be reformed and custom-made in accordance with business priorities, culture, and operating model. This forms the main driving force for the workforce analytics. But certain challenges faced are described below –
Problems associated with spreadsheets: Many businesses rely on spreadsheets, as it is conveniently available. But it is risky to use spreadsheets in analysis for decision making as reports are cumbersome to correlate and may contain inconsistent data. The frequency of errors resulting due to data entry errors and lack of data integrity needs rework which consumes the time of valuable resources. Hence a dedicated analytics system which includes key capabilities to address HR and business needs is required.
Ineffectiveness of current system: Most employers maintain typical enterprise resource planning (ERP) program to estimate basic HR metrics. These operational and transactional measures just provide ‘rear view mirror’ perspective of HR’s activities.
Fragmented data: Data quality and access is the fundamental problems for many organizations. Amount of data present might be enormous, but it is in an inconsistent state and is present in different places.
Above items reflect the need of proper data collection by asking right questions and then storing it in the desired format for further analysis. Overall, this constitutes the need for workforce analytics.
Guidelines to implement workforce analytics
Set your direction in-line with business strategy: Before starting the collection of employee-related data, HR must spend quality time to think about needs and goals of the organization. Then comes determining important aspects of analytics. This phase has to involve different stakeholders for selecting right direction. It is of organization’s interest to take the legal and cultural viewpoint of privacy laws.
Define approach: Subject matter experts can be approached in this step for seeking their opinions on method of data collection. Collection of right data solves a major problem of workforce analytics. So, this step forms a core part of the entire transformation. Methods to store data efficiently, analyze the data and creating visuals should be discussed and decided.
Start small: Setting up the business case as a small consulting project will constraint the initial costs incurred. The team involved must have a balance of skills including HR knowledge, data science understanding, and consulting experience. The scale of the team will be dependent on the project.
Grow your capability by taking actions based on insights: Slowly momentum should be built to exploit the potential of analytics. Insights from workforce analytics, then start helping leaders to quickly form teams for new projects. Building the capacity to scale will be decided based on the ROI generated by the initial phase. Ultimately analytics should become organization’s ability to stay well-informed of market changes.
Standard metrics
Workforce analytics can provide improved visibility of information to arrive at smarter decisions in a timely way. Analytics improve the manager’s ability to act in the interest of organization goals. Using predictive analytics, HR anticipates future workforce gaps and accordingly make effective decision to achieve goals of human capital management.
Below figure illustrates various possible outcomes of workforce analytics. All of which helps HR team to convert observation to insight and finally generate foresight.
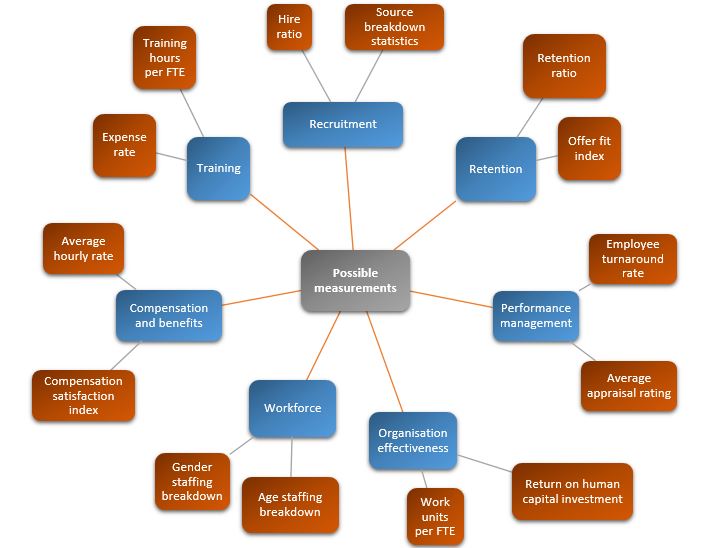
Workforce analytics in practice
Oracle studies the trends of employees leaving the organization and correctly defined prediction model. It identifies top performers who are predicted to leave the organization and why. This information drives the global policy changes to retain such employees. Oracle is expanding the use of this prediction model to make it more robust. If an organization decides not to retain, they plan the knowledge transfer well in advance and ensure smooth movement of resources.
AT&T utilized workforce analytics techniques to figure out the parameters which can be used to identify high performers. They demonstrated that ability to take initiative is far better to measure than academic records to figure out high performers.
Conclusion
Workforce analytics finds its analogy with – old wine in new bottles. The essential idea is not new to human resource professionals, but the analysis of a large amount of data is a new development. If analytics is not positioned as a substitute for human judgment, instead it is used as additional insight, HR team can create value for the organization.
Authored by Neeraj Chachlani, PGPM 2018, Great Lakes Institute of Management, Chennai